Janice distributed copies of ACSM tables 2-1 (CAD Risk Factors) and 2-2 (Recommendations), and Boxes 2-1 (Signs and symptoms) and 2-2 (Risk stratification).
Be able to look at a case study and evaluate the patient for risk factor status and symptoms. Be able to determine whether a physical exam and exercise test should be administered before prescribing an exercise program. Should a physician supervise the test?
Clinical Eval of CAD -- Sample case study
72 year old female (Betty) reports CP w/ exertion
Mother died of MI at 60 years of age
Former smoker (1ppd x 35 years), recently quit
Hypercholesterolemia, on lipitor
BP @ rest 148/94 mmHg
Glucose normal
Ht 60 in ; Wt 126 lb
Sedentary
Refer for stress EKG/cardiolite eval
Risk factor evalation: She has all risk factors but obesity (Her BMI is 24.8) and impaird fasting glucose.
Be able to calculate BMI for the exam!!! Here's Bette's example:
[126 lb / 2.2 = 57.3
kg] 60 in x 0.0254 = 1.52 M
57.3 kg/1.52 M2 =
24.8 kg/M2
Convert pounds to
kg:
Convert inches to
meters:
Calculate the ratio:
We’re lookin’ for…
EKG abnormalities…ST segment changes with exertion and recovery
Rate and rhythm
Hemodynamic response – BP
Clinical symptoms – CP, SOB
Functional capacity
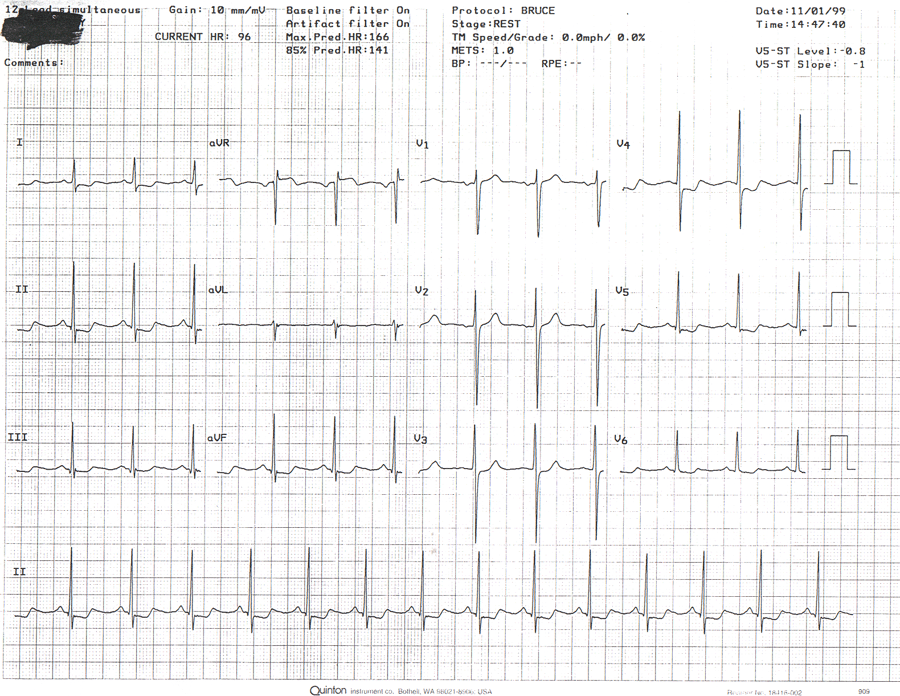
RESTING:

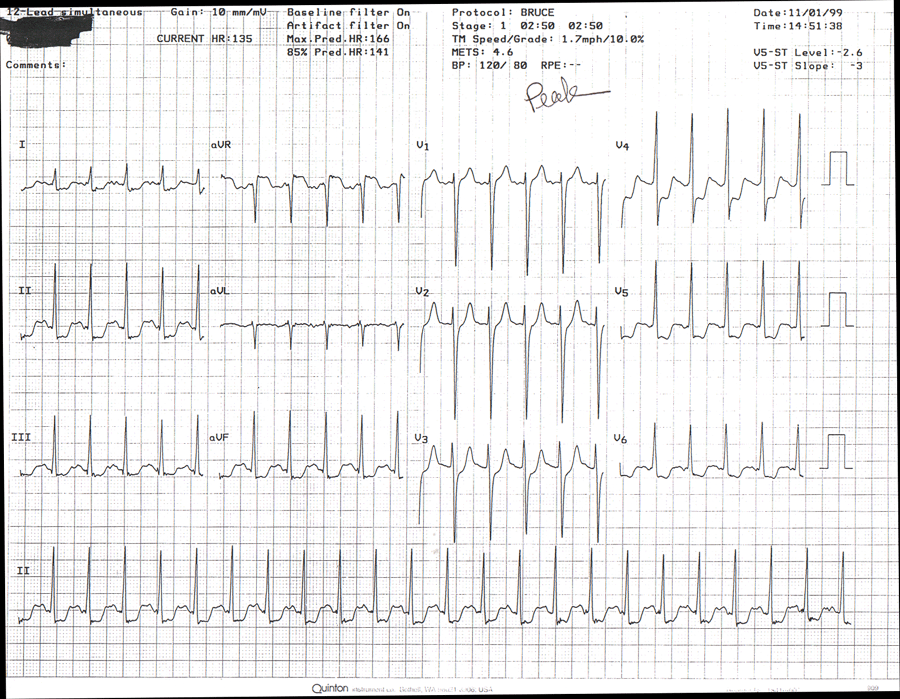
MAX
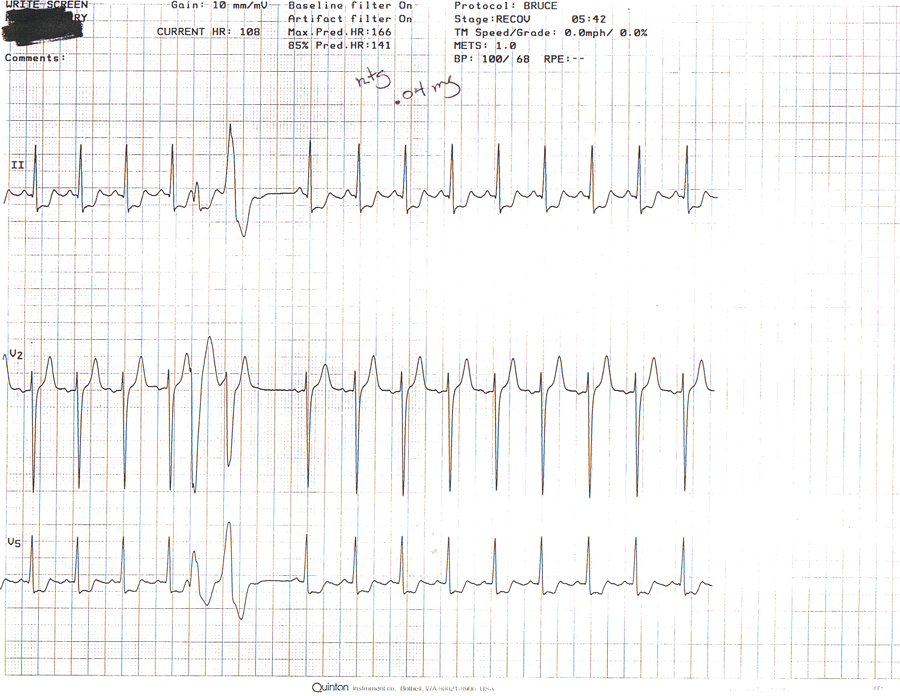
RECOVERY
Stress Test Summary
Resting: EKG shows NSR, Rate 96, BP 170/90Pt exercised for only 3 minutes on Bruce proto achieving 1.7 mph, 10% gr. Stopped due to SOB, severe CP, and hypotensive response. BP at max exercise was 120/80. Max HT was 135 BPM, 91% of age-redicted max.
At max exercise, we observed 2.3 mm horizontal and downsloping ST depression, which persisted during recovery.
During recovery CP, ST depression, and hypotension persisted, and a multiformed PVC couplet was observed. .04 mg NTG administered. CP and ST changes resolved at 18:00 of recovery
Conclusion: Clinically positive, Electrically positive, hypotensive hemodynamic response, very poor functional capacity. Refer for cardiac catheterization.
Thallium 201, a radioactive isotope is injected. Here's a sample interpretation:
Transient LV dilationSmall, mildly severe, completely reversible anteroapical defect
Moderately large and severe, reversible inferior and inferoseptal defect involving the basilar half of the inferior wall
LVEF was calculated 41% (gated)
Echo Doppler
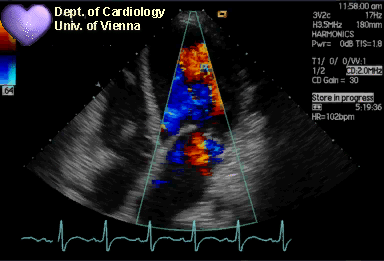
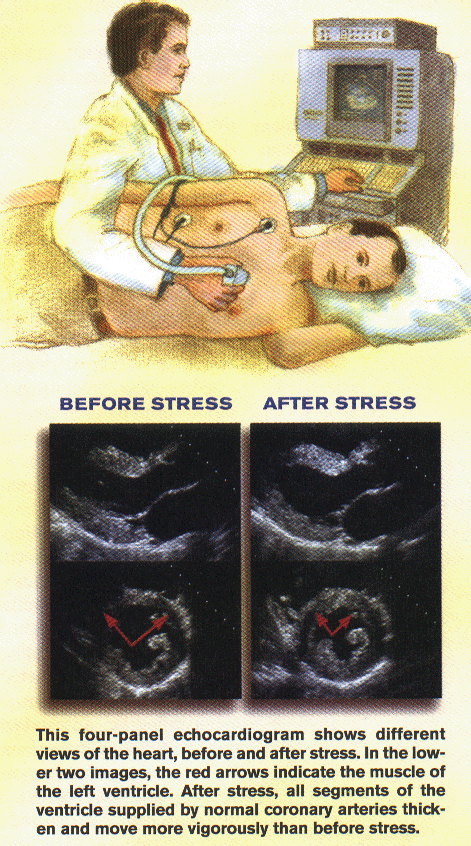
Stress Echo
Angiography:
PTCA:
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty: A balloon is inserted into the narrowed lumen and inflated. This compresses the plaque against the artery wall.A stent is often inserted to provide a framework!
Atherectomy can be conducted on hard calcified plaque using the an instrument called the Rotoblator.
CABG: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
The most invasive intervention to re-establish normal flow in the coronaries. Grafts may be taken from the internal mamary arteries, saphenous veins, or radial arteries.