Lecture plan
I. Social exchange models
Role of personality variables Costs and benefits (behavioral economy) What maintains behavior Personal gain vs. communal focus Reciprocity (Quid pro Quo)
Commentary:These have been generally called "behavioral models." They emphasize
constructs that implicate situational control of behavior, focusing on what
spouses do rather than on their personalities. The consequences of actions
are believed to account for more variance in satisfaction than personality
variables. They tend to be like business arrangements applied to "love."
People are often uncomfortable with this notion, that "love" is negotiated,
that people seek personal gain at low personal cost, etc. This approach
runs headlong into the voluntary choice, illusion of choice ideas that are
so prevalent. (Just read some of the postings to the Marriage list!) The
role of situational control of behavior is very important in these models.
These models do not spend a lot of time worrying about the past history of
people. The Halford et al. article tries to show the changes from the early
behavioral models (BMT) and the newer versions, as described in his article.
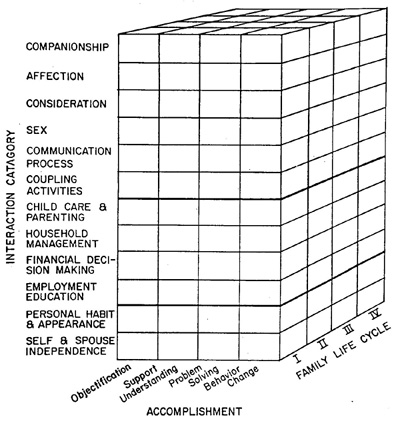
II. Performance Based Model (OMSP)The Oregon Marital Studies Program (OMSP)
model is divided into three major categories:

There are four areas of Accomplishment:
Content areas:
Stages of Family Life Cycle:
Pleasure Sine-Wave:
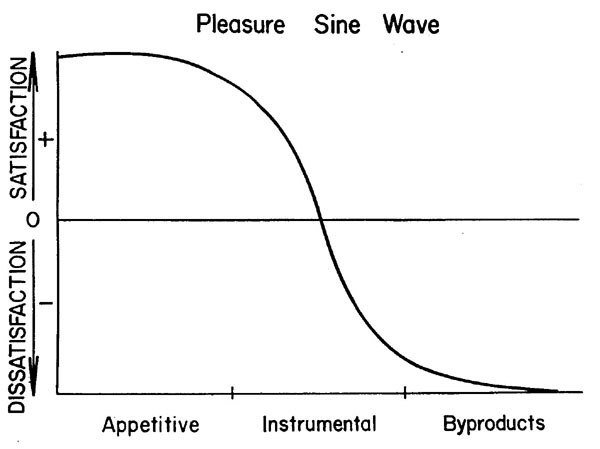
This is an important conceptual aide that derives from the OMSP model.
Marital satisfaction and dissatisfaction are not just bi-polar, but rather
they are separate dimensions. The absence of satisfaction is not
dissatisfaction! Be sure to copy the drawing of the pleasure sinewave.
III. Social Learning Conceptions
| Return to Main |