Cardiac
Conduction Defects
CV Physiology -- EMS
410/510
JL Radcliffe -- 30 January 2002
- Normal PR and QRS
intervals
- AV
blocks
- Bundle branch
block
Normal PR
and QRS intervals
Measuring
intervals: Note landmarks for pr, QRS, and QT
intervals.

The PR
interval:
|
Measure
from start of P to start of QRS.
WNL if 0.12-0.20 seconds (3-5 small boxes)
|

|
QRS
interval
|
Measure from
the start to the end of the QRS complex!
WNL = 0.1
seconds or less (2.5 small boxes or less)
|

|
AV
blocks
1st Degree
AV block
Features: P wave
for every QRS, but P-R interval >0.20 (>5 small
boxes)

2nd Degree
AV block
Two
classifications:
2nd Degree
AV block/ Wenckebach
Progressive
lengthening of PR interval until a QRS is
‘dropped!

2nd Degree AV
block/ Mobitz
PR intervals are
constant, but QRS is dropped suddenly.

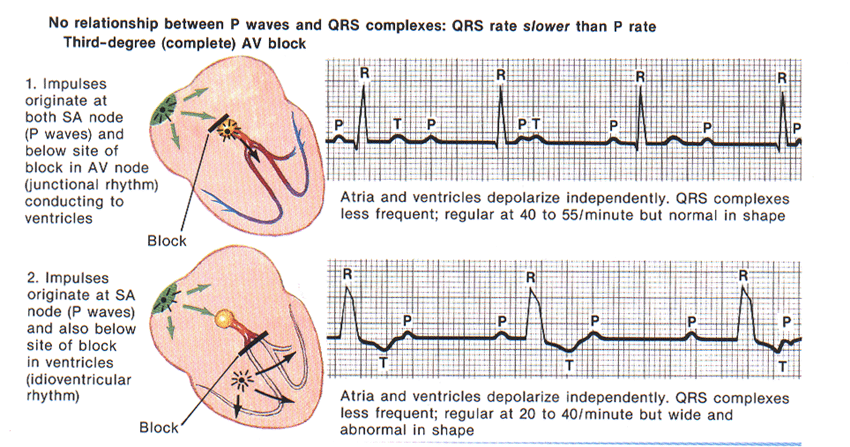
3rd Degree
AV block
Features: AV
dissociation! The P-P intervals are dissociated from R-R
intervals.
Escape rhythm below AV node paces at its inherent rate
Bundle
branch blocks
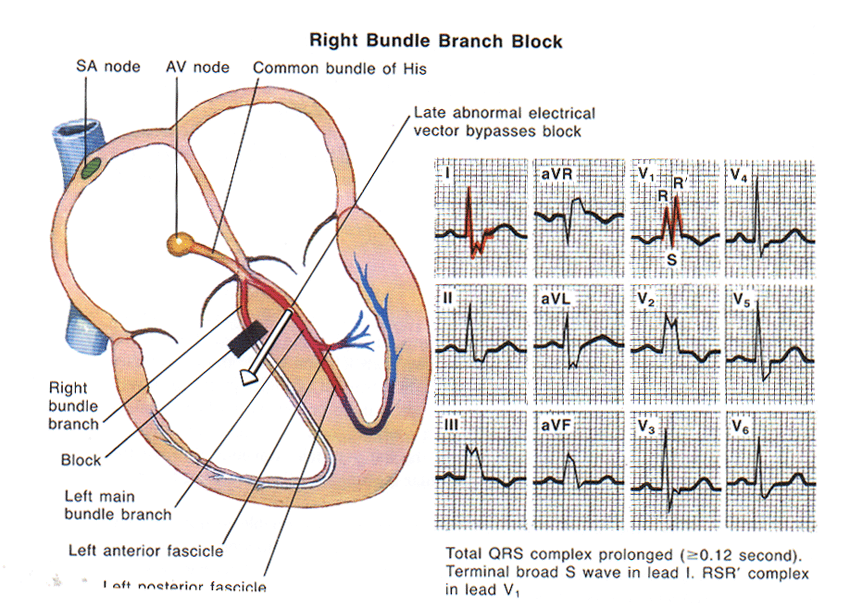
Right
BBB
Features: QRS 0.12
sec or more. RR’ in V1, V2
Left BBB
Features: QRS width
0.12 sec or more… Big S in V1 and wide R in V5 and other
lateral leads. ST segment abnormalities

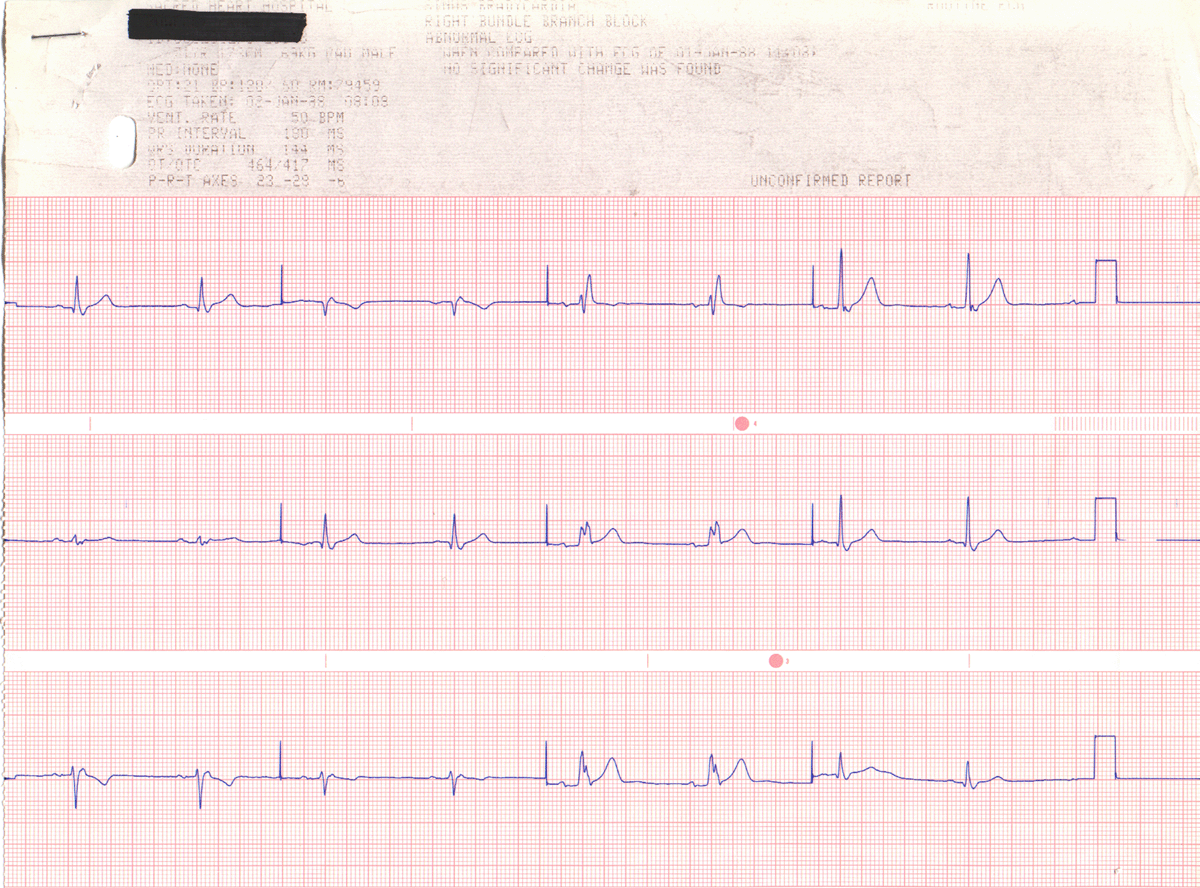
FOR THE GRAND FINALE...
Analyze the tracing below for:
Rate____________________
Rhythm____________________
Conduction:
pr interval
_______ sec.
QRS interval_______sec.
Other characteristics which confirm your suspision?
___________
Conclusion____________________________________________